Remote Sensing based indices for Detecting Forest Disturbance and Degradation in Northern Jordan (Jawarneh et al.).
Prof. Dr. Rana N. Jawarneh
Students : Kefah Harahsheh, Bushra Al-Balawnah, and Rudyna Abuhadba
Abstract:
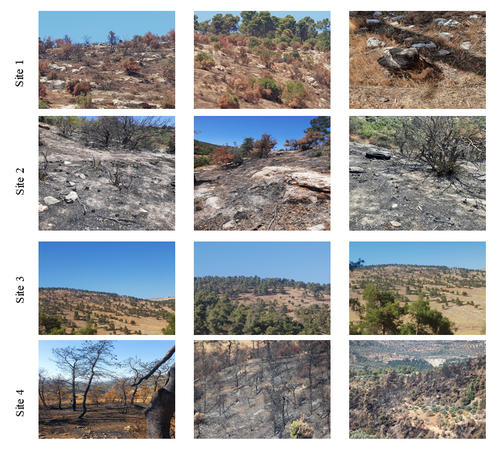
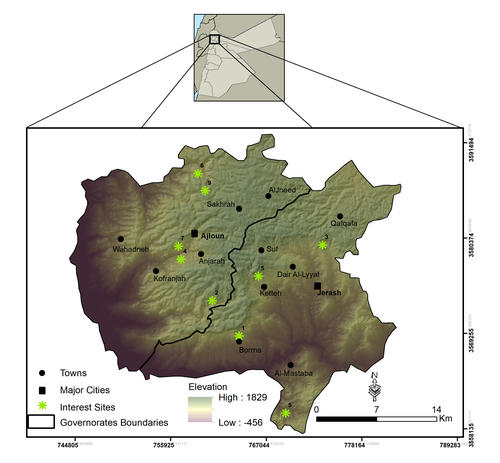
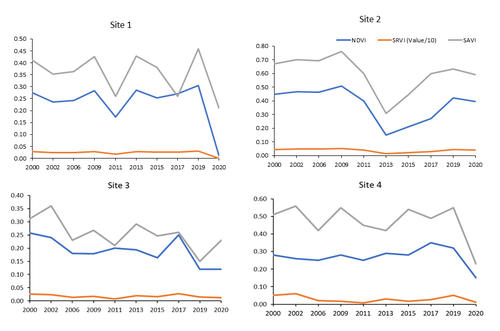
This study investigates long-term forest cover change in northern Jordan from 2000 to 2020 and highlights the main drivers affecting forest loss in the study area. The aim is to utilize remotely sensed-based approaches in tracking forest dynamics and present spatially explicit evidence on the impacts of wildfires, disease outbreaks, illegal cutting, and conversion to agriculture on Jordan's forest ecosystem. Forest cover dynamics were assessed using bi-temporal change detection from 2000 to 2020. The 2000 forest cover was extracted from the Jordan National Land Cover Dataset (JNLCD), while the 2020 forest cover was developed using Landsat-8 OLI image following the same mapping techniques used for the JNLCD. Leading factors affecting forest change in the study area were investigated by deriving t vegetation indices time-series (SR, NDVI, SAVI) in 9 different sites (pixels) from the Landsat Surface Reflectance Climate Data Records (CDRs). For validation, each site was observed, and photos were taken to document the change cause and impact on forest change. The results of change detection indicated a decrease in forest cover in northern Jordan from 69 km² in 2000 to 59 km² in 2020, with a relative decline of 15% over the past 20 years. At the governorate level, Ajloun lost 7 km², while Jerash lost 3 km² between the years. The results of the TS analysis of individual vegetation indices showed the impacts of main causes on forest change in northern Jordan. At the same time, it showed no or minimal change in vegetation values for site 9, which is in a forest reserve in Ajloun. This urges for expanding such protected areas to include more forested areas in Jordan. The findings of this study pinpoint the need for a national monitoring program and risk management strategy that integrate remotely sensed-based methods to preserve the limited forest ecosystem of Jordan.
Keywords: Forest degradation; Landsat CDRs; Time-Series analysis, change detection; vegetation Indices; Jordan.