Department of Earth Sciences
Service Navigation
Rendezvous of Moons as seen by Europe’s Mars camera HRSC
Europe's successful Mars High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) on the Mars Express satellite not only has an eye for the Red Planet, but also regularly observes the two moons of Mars, Phobos and Deimos, as well as other bodies in our solar system when interesting constellations arise.
Occultation of Jupiter and the Galilean moons by Deimos
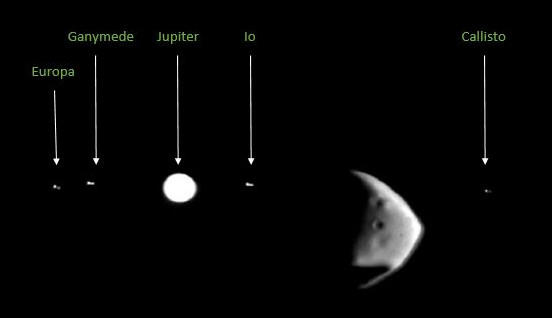
On February 14th, 2022, at orbit 22.895, was one of those occasions: The smaller of Mars' two moons, Deimos, slid in front of Jupiter and its four Galilean moons as seen from Mars Express. In this animation, Deimos is seen first occulting Europa and Ganymede, then Jupiter, and finally Io and Callisto. It was created from 80 images taken with HRSC's 985-mm telephoto lens called SRC. Such an observation is very rarely possible because Deimos must be exactly in the orbital plane of Jupiter's moons for it to be possible. These four largest moons of Jupiter are only visible as small white dots. Their distance from the camera is 745 million kilometers (that is 5 astronomical units, i.e. 5 times the distance between Earth and Sun!). Due to the difference in brightness to Deimos, they would not have been visible on the images next to the extremely bright Jupiter, if these images had not been contrast enhanced separately and locally at the positions of the moons. The slight up and down movements of Deimos are due to a slight swinging of Mars Express, which occur after the rotation of the satellite when pointing to a new target. The spacecraft swings a bit after each movement due to the swinging of its solar cells with a span of twelve meters as well as the seven and twenty-meter-long radar antennas.
Such images are, of course, not taken merely for aesthetic pleasure, but serve an important scientific purpose: the precise determination of the ephemerides of the Martian moons. Due to the tidal forces of Mars, both moon orbits are constantly changing.
Phobos moves toward Mars, Deimos away from it. Constant recalculation of their ephemerides is therefore essential. Since the position of Jupiter and its moons is known more precisely, they can be used as reference bodies in these images to determine the position of Deimos.
The picture shows the gas planet Jupiter and its moons Europa, Ganymede, Io and Callisto:
Youtube
Occultation of Jupiter and the Galilean moons by Deimos
Clip Information:
Occultation of Jupiter and the Galilean moons by Deimos. Orbit 22.895 on February 14th, 2022. The distance from Mars Express to Deimos is 17300 km, to Jupiter it is 754 million kilometers.
→ Title: Occultation of Jupiter and the Galilean moons by Deimos
→ Length: 00:20 min
→ Data: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin
→ Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin (CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO)
Deimos occultation by Phobos
Another example of such aesthetically valuable astrometry images can be seen in the second animation shown here: The larger and inner Martian moon Phobos pushes in front of Deimos. For this, 19 SRC images taken on 30 March 2022 were stitched together. The distance to Phobos here is 12.261 kilometers, that to Deimos 27.907 kilometers. The size difference of the two irregularly shaped bodies cannot be seen realistically from this perspective: Phobos measures about 27 kilometers on its largest axis, while Deimos measures a maximum of 15 kilometers across.
Calculating the orbits of the Martian moons is very difficult when viewed from Earth. The bright Mars outshines the moons, which are on top of that very close to their planet, so much that they are only observable with larger telescopes. An observation by a Mars camera with the Red Planet "in the back" is accordingly much easier and achieves far more exact results. Knowing the exact position of the moons in their orbits around Mars is essential, not least for the Japanese Martian Moons eXploration mission (MMX), which will place a lander on Phobos with European participation.
Clip Information:
Deimos occultation by Phobos in orbit 23.258 on March 30th, 2022.The distance from Mars Express to Phobos is 12.261 km, to Deimos it is 27.907 kilometers.
→ Title: Deimos occultation by Phobos
→ Length: 00:04 min
→ Data: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin
→ Credit: ESA/DLR/FU Berlin (CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO)
Youtube
Deimos occultation by Phobos
