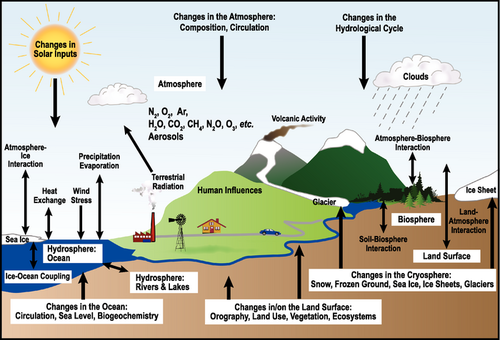
Climate and climate change
The global climate system is composed of atmosphere, hydrosphere (liquid water), cryosphere (ice and snow), lithosphere (soil and rock) and biosphere (plants and animals, including humans). The climate of a particular area is dependent on the complex nonlinear interactions between these components under the effects of solar radiation, the rotation of the earth and its orbital motion around the sun. The climate is usually defined in terms of a statistical description (mean and variability) of variables such as temperature and precipitation over a period of time ranging from a few years to millions of years. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) recommends 30 years as the minimum period for averaging these variables to ascertain variability. (CAP-NET 2009)